| 河南大学计算机操作系统实验四 | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › 管道 进程 › 河南大学计算机操作系统实验四 |
河南大学计算机操作系统实验四
|
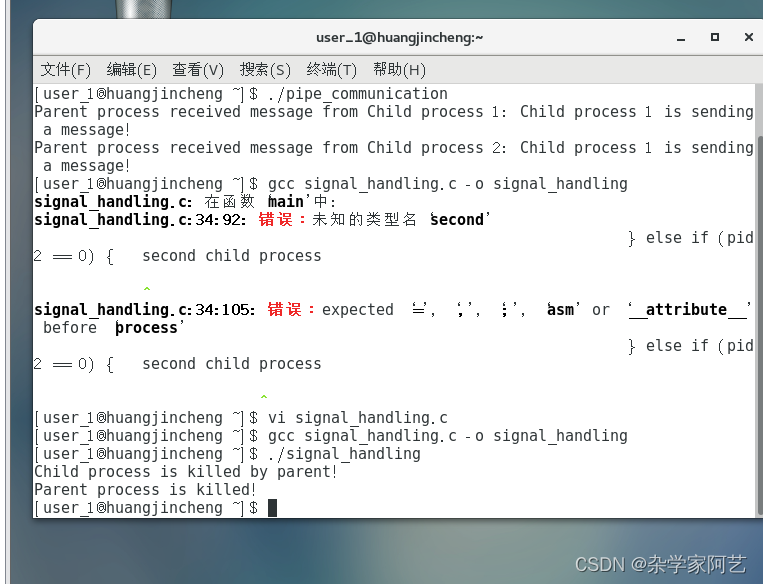
任务一:管道通信的程序 创建管道:使用 pipe() 系统调用创建一个管道,它返回两个文件描述符,一个用于写入,一个用于读取。 创建子进程:使用 fork() 系统调用创建一个子进程,子进程将会继承父进程的文件描述符,包括管道的文件描述符。 父子进程通信:父进程通过写入管道的文件描述符向管道中写入数据,子进程通过读取管道的文件描述符从管道中读取数据,实现了父子进程之间的通信。 代码如下: #include #include #include #include int main() { int fd[2]; pid_t pid; char buf[100]; if (pipe(fd) < 0) { perror("pipe error"); exit(1); } pid = fork(); if (pid < 0) { perror("fork error"); exit(1); } else if (pid > 0) { // parent process close(fd[1]); // close the write end of the pipe read(fd[0], buf, sizeof(buf)); printf("Parent process received message from Child process 1: %s\n", buf); wait(NULL); // wait for the first child process to finish read(fd[0], buf, sizeof(buf)); printf("Parent process received message from Child process 2: %s\n", buf); close(fd[0]); // close the read end of the pipe } else { // child process close(fd[0]); // close the read end of the pipe char* message1 = "Child process 1 is sending a message!"; char* message2 = "Child process 2 is sending a message!"; write(fd[1], message1, strlen(message1) + 1); write(fd[1], message2, strlen(message2) + 1); close(fd[1]); // close the write end of the pipe exit(0); } return 0; } 任务二:信号处理的程序 注册信号处理函数:使用 signal() 函数注册信号处理函数,指定当接收到特定信号时应该执行的处理函数。 接收信号:程序运行时可以通过发送信号(例如使用 kill 命令)来触发注册的信号处理函数。 处理信号:当接收到指定的信号时,注册的信号处理函数会被调用,程序会执行相应的处理操作。 代码如下: #include #include #include #include #include void sigint_handler(int signo) { printf("Received SIGINT signal from keyboard\n"); } void sigchld_handler(int signo) { if (signo == SIGCHLD) { printf("Child process is killed by parent!\n"); exit(0); } } int main() { pid_t pid1, pid2; int status; if ((pid1 = fork()) < 0) { perror("fork error"); exit(1); } else if (pid1 == 0) { // first child process signal(SIGCHLD, sigchld_handler); while(1) { // do something } } else { if ((pid2 = fork()) < 0) { perror("fork error"); exit(1); } else if (pid2 == 0) { // second child process signal(SIGCHLD, sigchld_handler); while(1) { // do something } } else { // parent process signal(SIGINT, sigint_handler); sleep(1); // wait for the user to send SIGINT signal kill(pid1, 16); kill(pid2, 17); wait(&status); printf("Parent process is killed!\n"); exit(0); } } return 0; } 对于多次运行产生不同结果的考虑: 多次运行上述程序可能会出现不同的结果,这是由于进程调度的随机性导致的。在父进程发送信号给子进程后,子进程可能会以不同的顺序响应信号,导致输出的顺序不同。此外,由于信号的异步性,子进程在接收到信号后的处理速度也可能不同,也会导致输出的顺序不同。这些都是导致不同结果的原因。 |
【本文地址】